Initial Investment and Payback Period
Key considerations when evaluating the financial benefits of installing a solar system is the initial investment required and the subsequent payback period. While the upfront cost of purchasing and installing a solar system can be significant, it is important to analyze the long-term savings it can generate. The cost of solar panels has been steadily declining in recent years, making them more affordable and accessible to homeowners and businesses alike. Additionally, there are various financing options available, such as solar loans or leasing arrangements, which can help spread out the initial investment and make it more manageable.
The payback period, which refers to the time it takes for the savings on energy bills to cover the cost of the solar system, depends on factors such as the system's size, the amount of electricity consumed, and the local electricity rates. In general, the payback period for residential solar systems typically ranges from 5 to 15 years. However, it's worth noting that the payback period can vary significantly depending on the specific circumstances. By conducting a thorough analysis of energy usage patterns and estimating the potential savings, homeowners can determine a more accurate payback period for their solar investment.
It is essential to consider the long-term financial benefits beyond the payback period. Solar systems have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years or more, during which they can continue to generate electricity and save money on utility bills. Once the initial investment is recovered, the ongoing savings can be substantial. In fact, solar systems can significantly reduce or even eliminate electricity bills, especially when combined with energy-efficient practices and appliances. This can result in considerable long-term savings and a notable increase in disposable income for homeowners and businesses.
While the initial investment required for installing a solar system may seem substantial, it is crucial to consider the potential long-term financial benefits. The payback period, typically ranging from 5 to 15 years, can vary depending on factors such as system size and energy consumption. Beyond the payback period, solar systems can continue to generate savings by reducing or eliminating electricity bills. By carefully assessing the initial investment and payback period, homeowners and businesses can make informed decisions about whether installing a solar system will ultimately save them money.

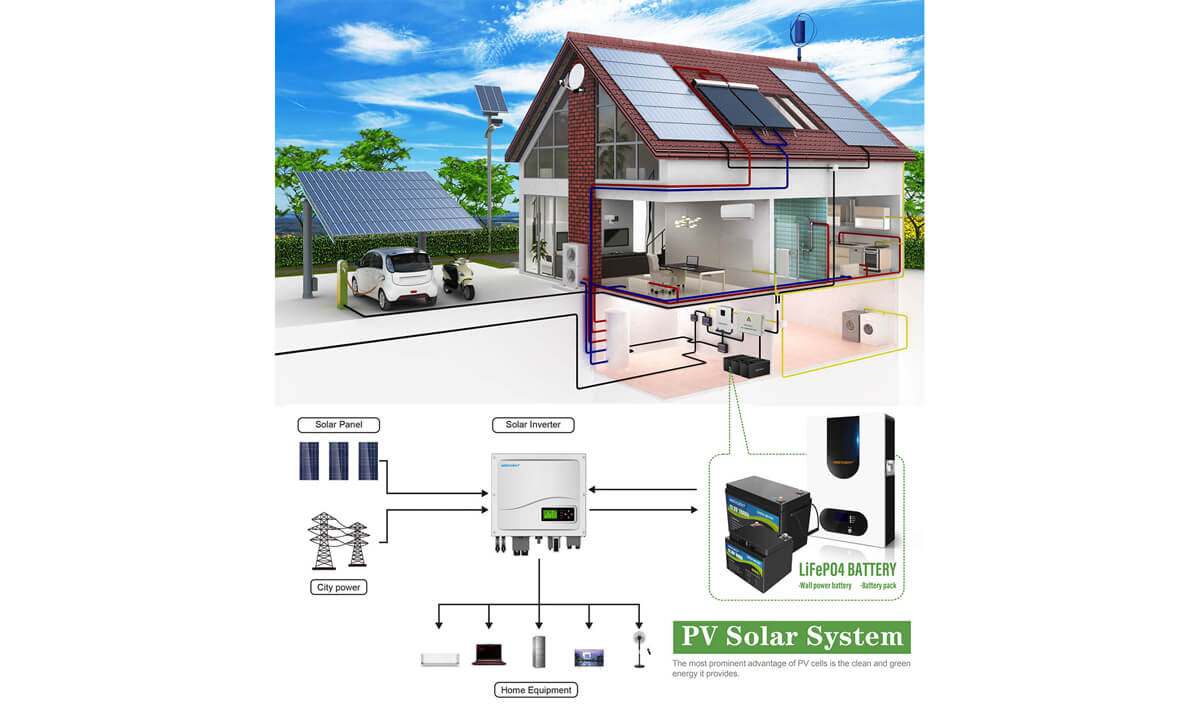
5KW HYBRID SOLAR SYSTEM
Reduction in Energy Bills
Primary financial advantages of installing a solar system is the significant reduction in energy bills. Solar panels generate electricity by harnessing the sun's energy, which can offset a considerable portion of a home's or business's electricity consumption. By utilizing solar power, homeowners and businesses can reduce their dependence on traditional grid electricity, resulting in substantial savings over time.
The extent of the reduction in energy bills depends on various factors, including the size of the solar system, the amount of sunlight available in the region, and the electricity consumption patterns. Generally, larger solar systems have the potential to generate more electricity, thereby reducing energy bills by a higher amount. In areas with abundant sunlight, solar panels can generate a substantial portion of the electricity needed, leading to significant savings.
Solar energy is a renewable resource, meaning that once the initial investment in solar panels is made, the electricity generated from them is essentially free. As electricity prices continue to rise, solar system owners can enjoy stable and predictable energy costs. This can provide long-term financial relief, as homeowners and businesses are shielded from the volatility of electricity prices and potential future rate hikes.
The installation of a solar system offers a remarkable advantage in terms of reducing energy bills. By generating electricity from the sun, solar panels can offset a significant portion of a home's or business's electricity consumption. The size of the solar system and the availability of sunlight play crucial roles in determining the extent of the reduction in energy bills. Additionally, solar energy provides long-term financial stability, protecting homeowners and businesses from rising electricity prices and ensuring predictable energy costs.
Tax Incentives and Rebates
Tax incentives and rebates are another important aspect to consider when assessing the financial benefits of installing a solar system. Governments at various levels, including federal, state, and local, often provide incentives to promote the adoption of renewable energy sources like solar power. These incentives can take the form of tax credits, rebates, grants, or other financial incentives, which can significantly reduce the overall cost of installing a solar system.
Most common types of incentives is the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which offers a tax credit equal to a percentage of the total cost of the solar system installation. As of the knowledge cutoff date of September 2021, the ITC provides a 26% tax credit. However, it's important to note that tax incentives and their specific terms can vary over time and depend on the jurisdiction. Therefore, it's essential to stay updated on the current incentives available in your area.
Many states, municipalities, and utility companies offer their own incentives and rebates to further encourage the adoption of solar energy. These incentives can include cash rebates, property tax exemptions, sales tax exemptions, or even performance-based incentives that pay solar system owners for the electricity they generate. By taking advantage of these incentives, homeowners and businesses can significantly offset the initial investment cost and accelerate the financial benefits of going solar.
Tax incentives and rebates play a crucial role in making solar energy more affordable and economically attractive. The federal Investment Tax Credit, along with state, local, and utility-based incentives, can substantially reduce the overall cost of installing a solar system. By leveraging these incentives, homeowners and businesses can maximize their savings and accelerate the payback period of their solar investment. It's important to consult with tax professionals or renewable energy experts to understand the specific incentives available in your area and to take full advantage of the financial benefits they offer.
Long-Term Financial Benefits
Installing a solar system offers numerous long-term financial benefits that extend beyond the initial investment and payback period. One of the key advantages is the potential for long-term energy cost savings. Solar panels generate electricity from a renewable source—the sun—which means that once the system is installed, the ongoing energy costs are significantly reduced. Homeowners and businesses can enjoy stable and predictable energy expenses, shielding themselves from the volatility and potential price increases of traditional grid electricity. Over the lifespan of a solar system, these long-term energy savings can amount to substantial financial benefits.
Another long-term financial benefit of solar energy is the potential to generate additional income through net metering or feed-in tariffs. Net metering allows solar system owners to send excess electricity back to the grid, effectively running their electricity meters backward. This surplus electricity is credited to their account, reducing future energy bills. In some cases, solar system owners can even earn money by selling their excess electricity to the utility company through feed-in tariffs. These additional income streams can contribute to the long-term financial viability of a solar investment.
Installing a solar system can increase the value of a property. Numerous studies have shown that homes equipped with solar panels tend to have higher resale values and sell faster compared to similar properties without solar installations. Buyers are increasingly attracted to homes with solar energy systems due to the potential for energy cost savings and environmental benefits. Therefore, investing in solar can provide long-term financial benefits by enhancing the marketability and value of a property.
The long-term financial benefits of installing a solar system are significant. They include ongoing energy cost savings, the potential for additional income through net metering or feed-in tariffs, and increased property value. Solar energy provides stable and predictable energy expenses, protects against rising electricity costs, and offers potential revenue streams. Moreover, homes with solar installations tend to have higher resale values. By considering these long-term financial benefits, homeowners and businesses can make informed decisions about investing in solar energy and reap the rewards over the system's lifespan.







