- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions
Climate change is one of the most pressing global challenges of our time, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to mitigate its impact. Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, trap heat in the atmosphere and contribute to global warming and climate change. The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes are the main sources of these emissions. To reduce greenhouse gas emissions, we need to transition to clean and renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, and adopt energy-efficient technologies and practices.
Solar energy is a key solution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Solar power systems convert sunlight into electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, making them a clean and renewable source of energy. According to the International Energy Agency, solar energy is the fastest-growing source of electricity in the world, and it is projected to be the largest source of electricity by 2035. By reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and transitioning to solar energy, we can significantly reduce our greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impact of climate change.
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions requires a collective effort from governments, businesses, and individuals. Governments can implement policies and regulations that encourage the use of renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies. Businesses can adopt sustainable practices and invest in clean energy sources to reduce their carbon footprint. Individuals can make small changes in their daily lives, such as reducing their energy consumption, using public transport, and eating less meat, to contribute to the collective effort of reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By working together, we can create a more sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.
- Increased energy security and independence
Energy security and independence are important goals for countries around the world. Relying on imported fossil fuels for energy can make countries vulnerable to price fluctuations, supply disruptions, and geopolitical tensions. By transitioning to clean and renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, countries can increase their energy security and independence. Solar energy, in particular, offers numerous benefits for energy security and independence.
Solar energy is abundant and widely available, making it a reliable source of energy for countries. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite resources and subject to price fluctuations and geopolitical tensions, solar energy is available everywhere and can be harnessed locally. This reduces countries' dependence on imported fossil fuels and enhances their energy security and independence. Moreover, solar power systems can be installed on a variety of scales, from small rooftop systems to large utility-scale projects, making them flexible and adaptable to different energy needs.
Solar energy also provides economic benefits for countries, creating jobs and stimulating local economies. The installation and maintenance of solar power systems require skilled workers, creating job opportunities in the renewable energy sector. Moreover, solar energy can reduce countries' reliance on imported fossil fuels, saving them money on energy imports and stimulating local economies. By transitioning to solar energy, countries can enhance their energy security and independence while creating economic opportunities for their citizens.
Increased energy security and independence are critical goals for countries around the world. By transitioning to clean and renewable energy sources, such as solar energy, countries can reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhance their energy security, and create economic opportunities for their citizens. Governments can play a crucial role in facilitating this transition by implementing policies and regulations that support the adoption of solar energy and other renewable energy sources.
- Job creation and economic growth
Job creation and economic growth are important benefits of the development of solar energy. The solar industry has been growing rapidly in recent years, and as a result, it has created numerous job opportunities worldwide. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, the renewable energy sector, including solar energy, employed 11.5 million people globally in 2019, with the solar sector alone accounting for 3.8 million jobs. These jobs span a wide range of fields, from manufacturing and installation to research and development, providing opportunities for skilled workers and entrepreneurs.
In addition to job creation, the development of solar energy can also stimulate economic growth. The installation and maintenance of solar power systems require a range of goods and services, including solar panels, solar inverters, energy storage batteries, and mounting systems, as well as engineering and construction services. This creates a supply chain of businesses that can benefit from the growth of the solar industry. Moreover, solar energy can reduce countries' dependence on imported fossil fuels, saving them money on energy imports and stimulating local economies. By investing in solar energy, countries can create a virtuous cycle of job creation and economic growth.
Solar energy can provide energy access to communities that lack reliable and affordable electricity. This can have a transformative impact on these communities, creating opportunities for economic development and improving quality of life. Solar energy can power small businesses, schools, and health clinics, enabling them to operate more efficiently and effectively. By bringing electricity to these communities, solar energy can create new markets, stimulate economic growth, and improve living standards.
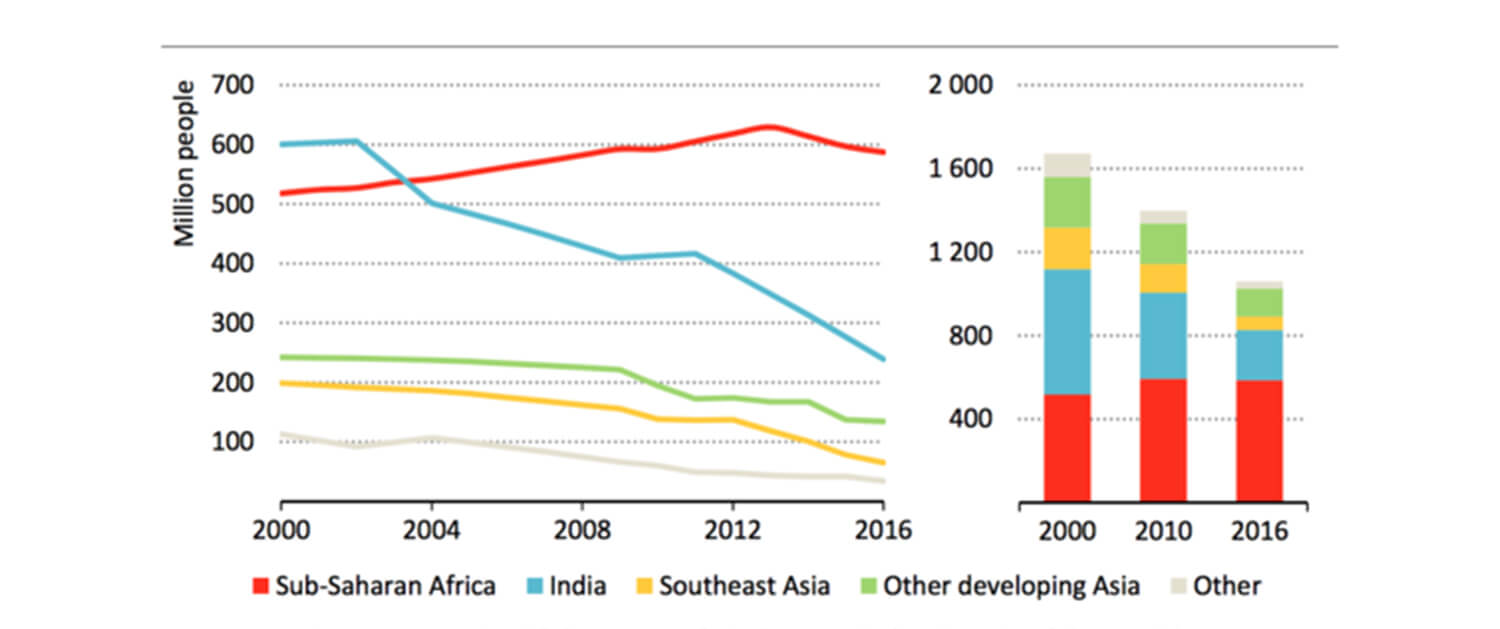
- Improved access to electricity in developing countries
Access to electricity is crucial for social and economic development, yet over 800 million people worldwide still lack access to electricity, primarily in developing countries. The development of solar energy offers a viable solution to this problem, as it can provide reliable and affordable electricity to communities that lack access to the grid. Solar energy is particularly well-suited for rural and remote areas, where extending the grid can be prohibitively expensive.
Solar energy systems, such as small-scale solar home systems, can be installed quickly and affordably, providing immediate access to electricity for households and small businesses. These systems can power basic appliances such as lights, fans, and mobile phone chargers, improving living standards and enabling productivity. Furthermore, solar energy can power larger systems such as schools and health clinics, providing access to education and healthcare services that are essential for social and economic development.
The development of solar energy in developing countries can also have a transformative impact on women and girls, who are often disproportionately affected by energy poverty. Lack of access to electricity can limit educational and economic opportunities for women and girls, as well as increase their exposure to health risks associated with traditional fuels such as kerosene. Solar energy can provide a clean and reliable source of energy for cooking, lighting, and other household needs, reducing health risks and improving quality of life.
The development of solar energy has the potential to improve access to electricity in developing countries, particularly in rural and remote areas where the grid is not available. Solar energy can provide immediate and affordable access to electricity for households, small businesses, schools, and health clinics, enabling social and economic development. Moreover, solar energy can have a transformative impact on women and girls, improving their access to education and healthcare services, and reducing their exposure to health risks associated with traditional fuels. Governments, international organizations, and the private sector can play a critical role in facilitating the development of solar energy in developing countries by providing financing, technical assistance, and policy support.









