Contents:
As the need for creative solutions in finding energy sources continues to increase, it is easy to regard solar panels as an abiding feature of modern architectural and energy systems. Such smart systems do not only utilize the free solar energy resource as a major source of energy for the entire building, but they also change the energy paradigm of the building in many other ways. This article seeks to address all functions, merits, aspects, and upkeep of solar panels and especially their relevance to the buildings.
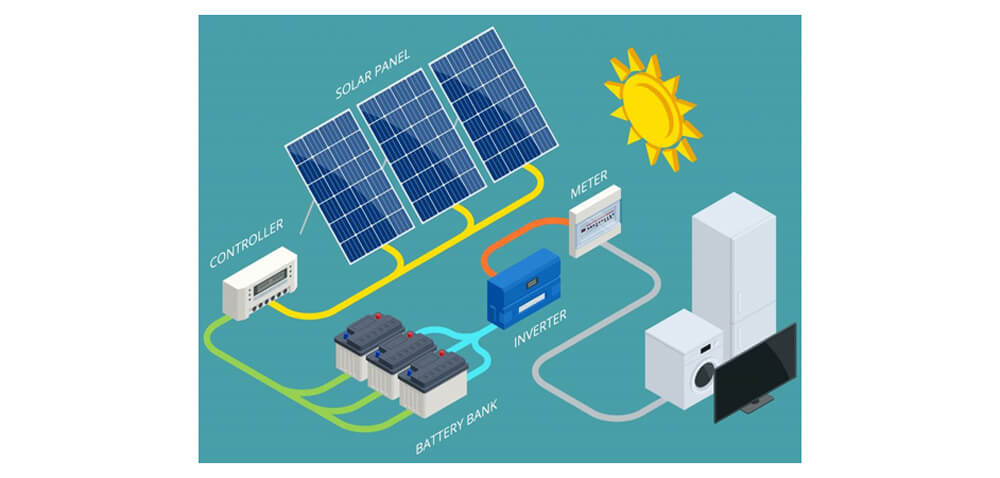
How Solar Panels Work
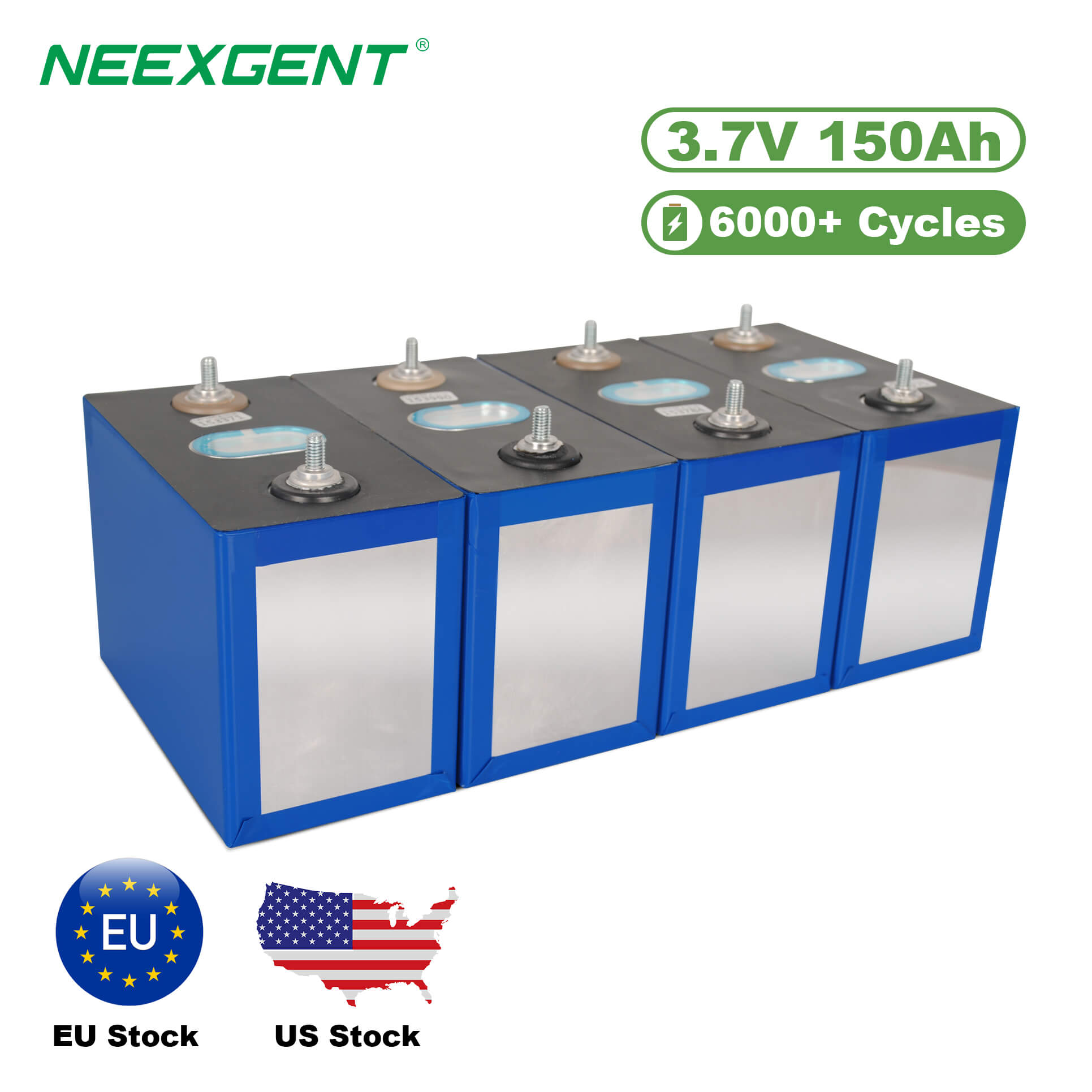
The solar panels (Photovoltaic (PV) panels) are devices which incorporate the photovoltaic effect to convert solar energy into electrical energy. The sunlight received by the solar cells installed on the panels excites the electrons and the electric current is produced. This process starts on an atomic scale where solar rays made up of photons strike molecules in the solar cell and release electrons thereby allowing them to move through the medium and produce electrical energy in the form of direct current (DC). This electricity is passed through an inverter that changes the produced current into alternating current for use with the electrical appliances in the facility.
Solar Panels for Buildings Advantages
1. Energy Independence
Being able to produce one’s own energy is one of the leading benefits of putting solar panels on the building. The buildings are therefore able to save a great deal of money on electricity by generating their own power from solar energy cut back on the use of external energy services significantly. This enhances energy security to the buildings especially during the hot seasons when energy demand is at its peak or during storms and other natural calamities.
2. Cost Effectiveness Analysis
In the case of solar panels, the costs incurred in acquiring them are rather high, although when considered in a time frame of years, the returns made are much higher than the respective costs. In most areas people and companies are able to greatly reduce their electricity using bills and as many geographical areas are offering affordable clean energy, the associated costs to one’s pocket are becoming less prohibitive. Additionally, net metering benefits individuals as any excess energy, once generated, can be given back to the grid at a credit that the owner will earn on their bill.
3. Impact on the Environment
Solar panels are very instrumental in conserving the environment, particularly in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. Through using renewable energy sources, buildings can create less of a carbon footprint and help improve air and water conditions. The cleanse in the air would be a big plus to not just the environment but also complement other trending needs of the present day consumers of the need to provide cleaner facilities thus improving the standing of the facility.
4. Higher Resale Value
That being said, potential buyers of residential properties fitted with solar panels are mostly willing to pay a premium for the case. With an increasing number of purchasers wanting to invest in energy efficient houses and even commerce premises, integrations of solar systems into building designs become an added advantage to the sale of the building. It has been established that homes with solar system installations command a higher resale value than those without making solar systems a reasonable cost to homeowners.
5. Low Demands for Upkeep
When it comes to solar panels, minimal upkeep is required as they are constructed in such a way as to last many years with their use. The majority of the systems come with performance guarantees ranging between 20 and 25 years and because of their good design, weather changes do not have adverse effects on them. More frequently than not, solar panel operation only requires cleaning and partial maintenance of the elements. Hence, the panels are efficient enough for the building owners.

Installation Aspects
1. Type and degree of roof angle
Roof angle and facing direction are some of the factors that determine how fast and effectively solar panels will work. It is normal for south-facing roofs to receive large sums of solar radiation, from sunrise to sundown, while roof pitch decides how much sunlight panels can receive. In addition to the above, flat type roofs, which can also carry solar panels somewhat, will have to use supplementary mounting hardware to tilt panels for better sun exposure.
2. Legal Aspects and Local Benefits
Knowing local building codes, zoning laws, and incentives is also important before proceeding with the installation. Many areas offer tax breaks, safety casseroles, and reimbursements, at least, for now, commercial use of solar power is permitted and thus less true building owners are discouraged from operating it financially.
3. System Size and Energy Needs
Choosing the correct cover, i.e., the size of the solar panel systems, will enable the building’s energy consumption to be satisfied. Energy audits, which assist in evaluating the present use of energy and help in defining the appropriate extent of the system, are necessary. It protects the clients and ensures that the solar installation would efficiently meet the energy demands of the construction.
4. Financing Options
Various ways such as the direct way, leasing, and power purchase agreements (PPA) can be used to install solar panels. Each type has pros and cons which are very significant to the owners of the buildings because their financial proposals and aspirations can motivate one to go for the best offer.
Maintenance of Solar Panels
Maintenance of solar panels is not complicated and includes several basic procedures:
1. Scheduled Maintenance
Awning pollution, dust, and bird feces can present themselves on solar panels affecting sunlight transmission and productivity levels. In areas that bear the brunt of dirt and or harsh rainfall, there is a need for cleaning up these surfaces with a frequency of once or once and a half every year.
2. Administration of Maintenance
Keeping up with administration usually involves undertaking maintenance of some of the method to put it simply, regular maintenance is housed within undertakings. Continuous poll of an impact is crucial for detecting the possibility of impact even before it occurs something like unsettled or tattered wires, broken panes, overshadows of trees with thick foliage, and tamed personnel. To help ease such components and breakdowns, one can hire services; the system will not malfunction since it will be attended to on time and only the minor repairs will be required.
3. Control of Operation
Most solar panel systems for the current buildings are embedded with control devices so that energy production activities can be measured in the course of building energy utilization. This information is considered extremely beneficial particularly for knowing why the current usage is not optimum thanks to the effectiveness of the system thereby making the investment quite worthwhile.

Conclusion
Apart from being an energy source, solar panels reflect an attitude towards energy use and energy conservation that is built in rather than bolted on. There are considerable reduction costs, increases in property value and benefits to the environment through the use of solar panels which harness clean energy. As more technologies become available and more buildings start using such technologies, the effect on energy consumption and the environment will be positive.
Where to buy solar panels should be concluded because it requires both monetary efforts and principle values. The more the buildings utilize renewable energy technologies, the more they inspire communities and industries around the world that it is possible to innovate, grow the economy, and have a better and greener world in the future.
Related Questions
How is the working of solar panels on a building to be described?
Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity by utilizing the photovoltaic effect, in which light carries energy that begins moving electrons located inside the solar cells – electricity and hence an energy supply for the building is generated.
What are solar panels used for?
The primary focus of solar panels is to capture solar energy and covert it into electrical energy, which is a cleaner alternative to fuels thus lowering energy costs.
How do buildings utilize solar gain?
The term solar gain refers to the degree in which the temperature of a building rises due to sunlight in the building. It can include the application of passive solar design which assists in heating and reducing heating costs.
What is currently the main drawback of solar energy?
The main concern with solar energy persists still – that of its intermittent nature; energy is only produced during daylight, increasing the need for effective means to store that energy.
Are solar panels a risk to the environment?
Yes, solar panels have positive impacts on the environment fuel saving and reduces carbon emissive pollutants but there are impacts related to the process of the solar panel from the materials used and their disposal.








