Recently, the demand for advanced battery technologies has risen due to quick rise in electric vehicle (EVs), renewable energy storage systems and portable electronic devices. Some of the leading chemistries include Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) and Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) batteries. Every type has its unique advantages and disadvantages, which make them suitable for different applications. Going through this article will give you an insight into the characteristics, performance, and applications of LFP and NMC batteries so that you can understand the differences between these two types of batteries and select the right technology for your needs.
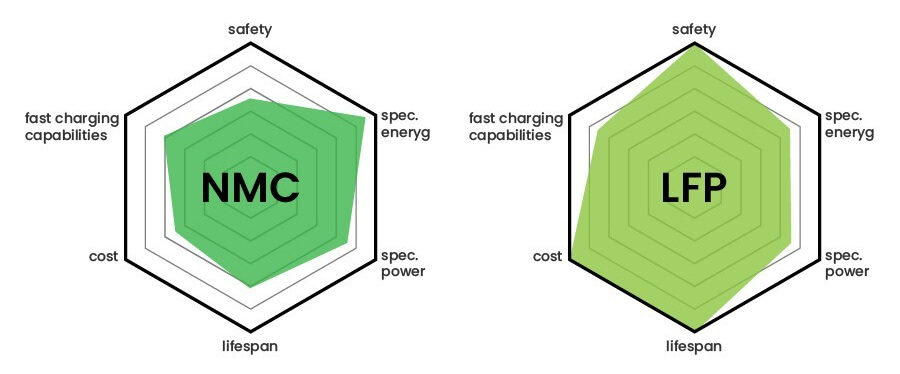
Overview on LFP and NMC Battery
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) Batteries
These batteries use lithium iron phosphate as their cathode. They are known for their stability, safety, and long cycle life. The main features of LFP batteries include:
Safety: In comparison with other lithium-ion battery types like LiCoO2 cobalt oxide cells,the thermal profile is stable minimizing overheating; therefore preventing possibility of thermal runaway enhancing safety specifically within high temperature environments.
Cycle Life: Usually LFP batteries have longer cycle lives extending to 2000-5000 charge/discharge cycles depending on usage conditions. This makes them ideal for applications where they are cycled frequently.
Environmental Impact: LFP batteries do not contain heavy cobalt, which is a harmful metal. This makes them friendlier to the environment.
Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) Batteries
The cathodes of NMC batteries are made using a combination of nickel, manganese and cobalt. They are versatile and known for their high energy density. Some key features of NMC batteries include:
- Energy Density: Compared to LFP batteries, NMC ones have a higher energy density that can fit more storage into a smaller and lighter package. This property is particularly useful in electric vehicles where weight and space are vital.
- Performance: As such, NMC batteries can provide more power than LFPs to meet fast charging applications such as those found in electric vehicles or power tools.
- Customizability: For optimal performance characteristics, the ratio of nickel, manganese, and cobalt can be adjusted thereby enabling manufacturers to tailor NMC batteries for various applications.
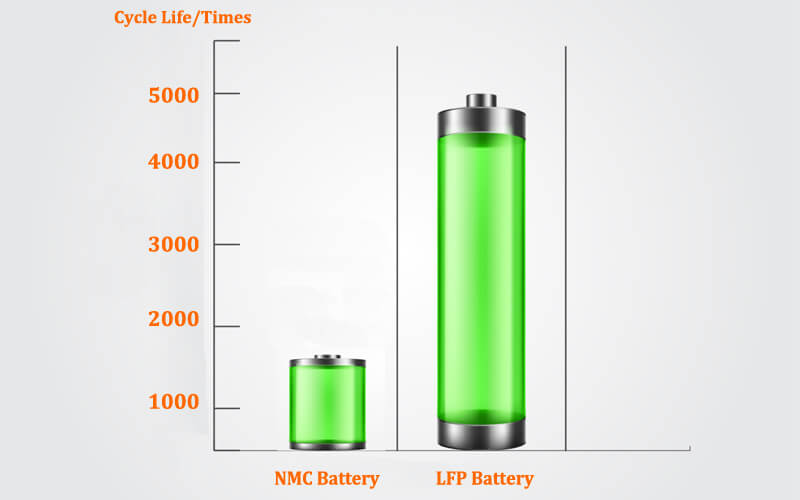
Performance Comparison
1. Energy Density
Comparatively, the two types of battery have a significant difference in energy density. LFP has an energy density ranging between 90 and 160 Wh/kg while NMC can have an energy density of 150 to 250 Wh/kg. This makes NMC more suited for use where weight and space are limited like electric vehicles and portable electronics.
2. Cycle Life and Stability
In terms of cycle life, LFP batteries are usually superior to NMC batteries. In general, NMC batteries last around 1000-2000 cycles while their LFP counterparts can take on 2000-5000 cycles. Such long-life battery cells are desirable for applications where they get frequently charged and discharged as in storage systems for renewable energies.
3. Temperature Performance
At high temperatures, these batteries perform well without the fear of thermal runaway. For instance, LFP is stable over a wider range of temperature compared to NMC which is usually problematic under very hot or cold conditions thereby needing careful control over its temperature conditions. These characteristics make it preferable to use LFP batteries in high temperature regions or when there are difficulties with thermal management.
Application of LFP Battery
- Energy Storage Systems: LFP batteries are widely used in stationary energy storage systems because they have a long cycle life and are safe. These batteries help store energy from renewable sources such as solar and wind power.
- Electric Buses and Commercial Vehicles: The safety and lifespan of LFP batteries make them the best option for electric buses and commercial vehicles which need reliable energy sources that will last long.
NMC Battery Application
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): NMC batteries are preferred over other types for EV’s as they exhibit high power output capacity as well as density, resulting in enhanced range capabilities and short charging times.
- Consumer Electronics: Among other things, NMC batteries find application in laptops, smartphones, etc. where performance and energy density cannot be compromised.
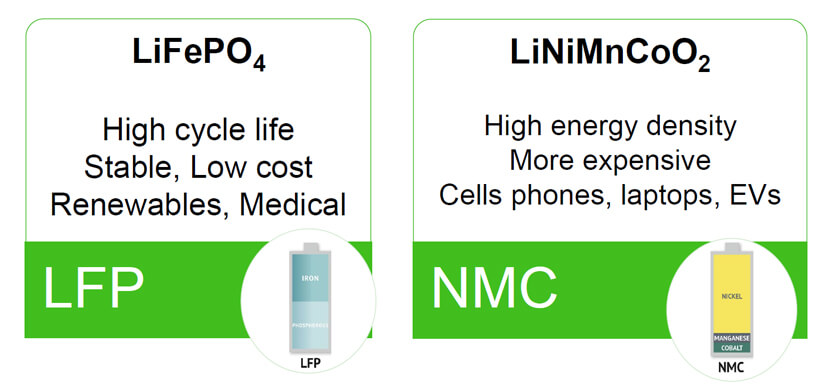
Distinct advantages of both LFP and NMC batteries make them suitable for different applications. For example, LFP batteries are highly recommended in energy storage systems and electric buses due to their safety, stability, and long cycle life. However, NMC batteries are great in terms of energy density as well as power output which makes them an ideal choice for electric vehicles and portable electronic devices.
Eventually, the use of either LFP or NMC battery depends on certain application requirements such as safety issues about the usage of energy, environmental considerations as well as energy needs. These developments will see both LFP and NMC batteries playing significant roles in advancing into the future of energy storage and electrical mobility solutions.








