1. Understanding Class A-graded LiFePO4 Batteries: Learn the Basics
LiFePO4 batteries, also known as lithium iron phosphate batteries, are a type of lithium-ion battery that have gained popularity due to their superior performance and safety features. Understanding the basics of Class A LiFePO4 batteries is crucial for making an informed decision when choosing a battery for your specific needs.
Understanding Class A LiFePO4 batteries is knowing their chemistry and advantages. LiFePO4 batteries use lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material, which provides excellent thermal stability and high thermal runaway threshold, making them inherently safe compared to other lithium-ion batteries. They are also known for their long cycle life, which means they can be charged and discharged numerous times without significant degradation in performance. Additionally, LiFePO4 batteries have a higher thermal and chemical stability compared to other lithium-ion batteries, reducing the risk of thermal runaway or combustion, making them a safer choice for many applications.
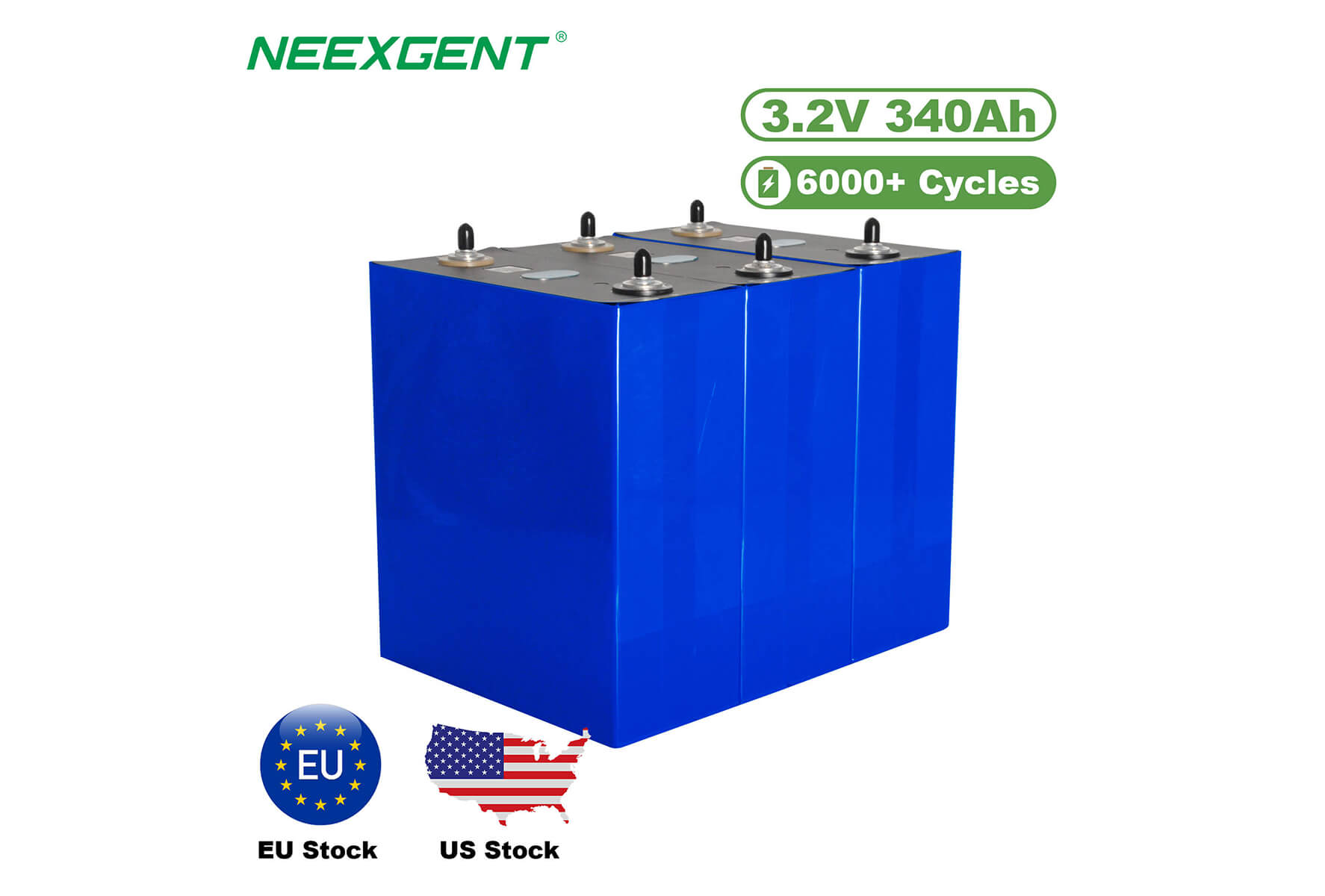
Another important aspect of understanding Class A LiFePO4 batteries is knowing their characteristics, such as voltage, capacity, and discharge rate. LiFePO4 batteries typically have a nominal voltage of 3.2 volts per cell, which is lower than other lithium-ion batteries. This lower voltage can impact the design and compatibility with certain devices or systems, and needs to be considered when choosing a battery for a specific application. However, LiFePO4 batteries often have higher capacity compared to other lithium-ion batteries, making them suitable for high-energy applications that require long run times. They also have a relatively low self-discharge rate, which means they can hold their charge for longer periods of time, making them ideal for applications that require standby power.
In summary, understanding the basics of Class A LiFePO4 batteries is crucial for making an informed decision when choosing a battery for your specific needs. Knowing their chemistry, advantages, characteristics such as voltage, capacity, and discharge rate, can help you determine if LiFePO4 batteries are the right choice for your application. Their superior safety features, long cycle life, and high thermal and chemical stability make them a popular choice for various applications, ranging from electric vehicles and renewable energy systems to portable power solutions and more.

2. Capacity and Voltage: Determining Your Power Requirements
Determining the power requirements of your specific application is a critical step in choosing a Class A LiFePO4 battery. Capacity and voltage are two key factors that need to be considered in this process.
Capacity refers to the amount of energy that a battery can store and is typically measured in ampere-hours (Ah) or watt-hours (Wh). It is an important parameter as it determines how long a battery can power a device or system. To determine the capacity needed for your application, you need to assess the energy requirements of your device or system. Consider factors such as the power consumption of the device, the duration of operation, and any potential peak power demands. It's important to choose a battery with a capacity that can comfortably meet your power requirements without being overburdened or constantly depleted, as over-discharging a battery can adversely affect its lifespan.
Voltage is another crucial factor to consider when determining your power requirements. Class A LiFePO4 batteries typically have a nominal voltage of 3.2 volts per cell. However, multiple cells can be connected in series or parallel to achieve higher voltages or increased capacity, respectively. It's essential to choose a battery with the appropriate voltage that matches the voltage requirements of your device or system. Using a battery with the wrong voltage can result in inefficient performance or even damage to the device or system.
When determining your power requirements, it's important to strike a balance between capacity and voltage. Choosing a battery with a higher capacity may result in increased runtime but could also increase the size, weight, and cost of the battery. On the other hand, choosing a battery with a higher voltage may allow for a smaller and lighter battery pack, but it may not provide sufficient capacity for longer runtime. Therefore, it's crucial to carefully evaluate the power requirements of your specific application and choose a Class A LiFePO4 battery that offers the right combination of capacity and voltage to meet those requirements effectively.
Determining the power requirements of your application is a crucial step in choosing a Class A LiFePO4 battery. Consider the capacity and voltage requirements of your device or system, and strike a balance between the two to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the battery. It's always recommended to consult with a qualified engineer or battery expert to ensure you select the right battery for your specific needs.

3. Quality and Safety: Evaluating Battery Manufacturers and Brands
- Reputation and Experience: Look for battery manufacturers and brands with a solid reputation and extensive experience in the industry. A manufacturer with a proven track record of producing high-quality batteries is more likely to provide reliable and durable products. Research the manufacturer's history, customer reviews, and certifications to gauge their reputation and experience.
- Battery Testing and Certification: Quality battery manufacturers conduct rigorous testing and certification processes to ensure that their batteries meet industry standards for performance and safety. Look for manufacturers that comply with international standards such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certifications, which indicate that their batteries are thoroughly tested and meet strict quality and safety requirements.
- Battery Materials and Construction: The quality of materials and construction used in a battery can greatly impact its performance and safety. Look for manufacturers that use high-quality materials and follow stringent manufacturing processes to ensure consistency and reliability. For example, Class A LiFePO4 batteries should use genuine lithium iron phosphate cathode materials and have proper cell assembly and protection against overcharging, over-discharging, and short-circuiting.
- Safety Features: Safety is a critical factor when evaluating battery manufacturers and brands. Look for manufacturers that prioritize safety by incorporating features such as built-in battery management systems (BMS) that monitor and protect against overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, and overheating. BMS plays a crucial role in protecting the battery and ensuring safe operation, so it's important to choose batteries from manufacturers that prioritize safety features.
- Customer Support and Warranty: Evaluate the customer support and warranty offered by the battery manufacturer. A reliable manufacturer should provide responsive customer support, clear product documentation, and a reasonable warranty period for their batteries. A good warranty can give you peace of mind and protect your investment in case of any manufacturing defects or issues with the battery.
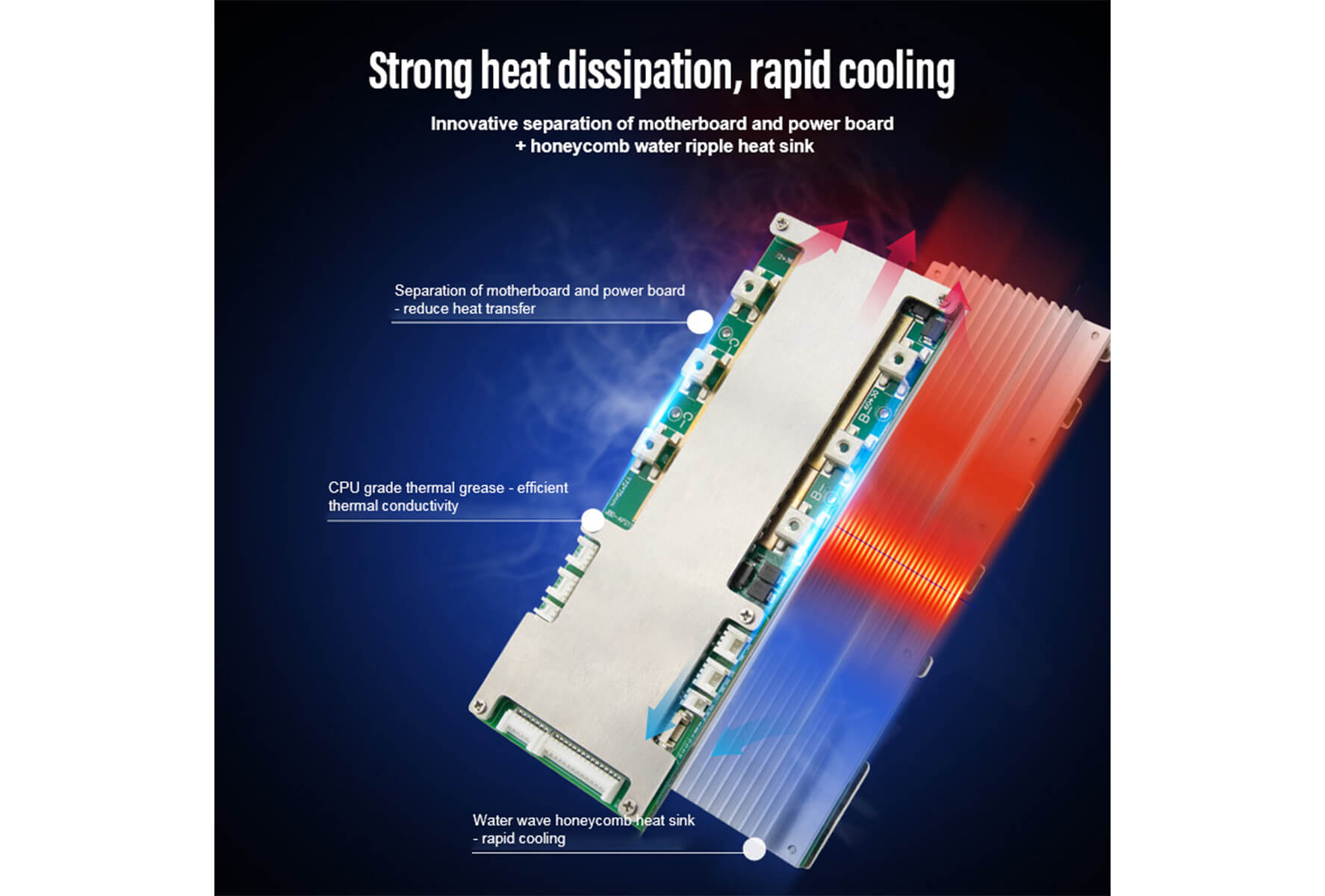
4. Battery Management System (BMS): Importance and Features
The Battery Management System (BMS) is a critical component of a Class A LiFePO4 battery that plays a crucial role in managing and protecting the battery's performance, safety, and lifespan.
- Safety: One of the primary functions of a BMS is to ensure the safety of the battery and the surrounding system. It monitors the battery's voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge (SOC) to prevent overcharging, over-discharging, overcurrent, and overheating. A BMS also protects against short-circuiting, reverse polarity, and other potential hazards, ensuring safe operation of the battery and minimizing the risk of accidents, fires, or damage to the battery.
- Performance Optimization: A BMS helps optimize the performance of the battery by maintaining the battery within its optimal operating conditions. It ensures that the battery is charged and discharged properly, preventing imbalances among cells and maximizing the battery's capacity and lifespan. A BMS also helps manage the state of charge (SOC) of the battery, preventing overcharging or over-discharging, which can adversely affect the battery's performance and lifespan.
- Cell Balancing: Class A LiFePO4 batteries are typically composed of multiple cells connected in series or parallel. A BMS monitors the voltage of each individual cell and performs cell balancing to ensure that all cells have similar voltage levels. Cell balancing helps equalize the charge and discharge levels of each cell, preventing overcharging or over-discharging of individual cells, which can lead to capacity imbalances and reduced battery performance.
- Communication and Monitoring: Many BMS systems come with communication interfaces, such as CAN (Controller Area Network) or RS485, which allow for remote monitoring and control of the battery. This enables real-time monitoring of battery parameters, such as voltage, current, temperature, SOC, and alarms, which can provide valuable information for system diagnostics, maintenance, and performance optimization.
- Fault Detection and Alarms: A BMS is equipped with fault detection mechanisms that can detect abnormalities in the battery's performance, such as overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, and overheating. When a fault is detected, the BMS triggers alarms or warnings to alert the user or the system, allowing for timely actions to prevent potential issues and ensure safe and reliable battery operation."









