Energy Access and Poverty Alleviation:
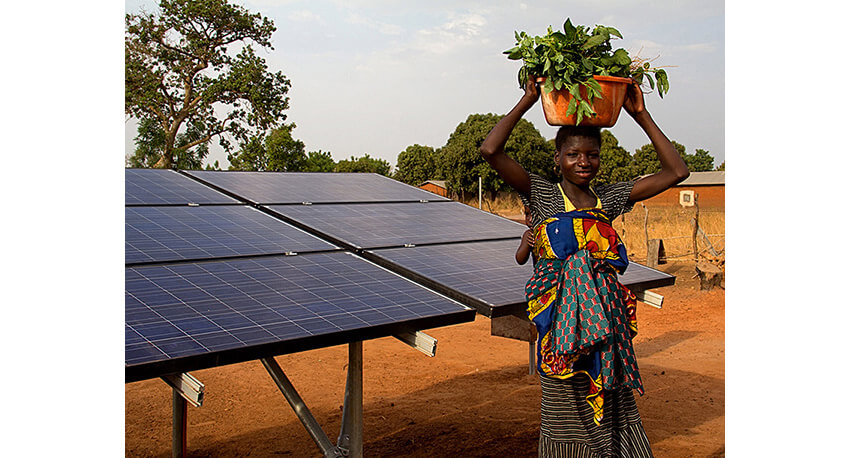
Solar energy systems have a significant role to play in addressing energy poverty in developing countries. By providing reliable and affordable electricity, reducing reliance on traditional fuels, and improving livelihoods through increased access to modern energy services, solar energy can contribute to poverty alleviation, empower communities, and foster sustainable development in some of the most underserved regions of the world.
One of the key roles of solar energy in addressing energy poverty is providing reliable and affordable electricity to underserved communities. Solar energy systems, such as solar home systems and mini-grids, can be deployed in remote and off-grid areas where grid extension is not economically viable. These systems can provide electricity for lighting, powering appliances, and running small businesses, enabling communities to access modern energy services that can significantly improve their quality of life. Reliable access to electricity also opens up opportunities for education, healthcare, and economic activities, contributing to poverty alleviation by empowering communities to break the cycle of poverty.
Solar energy also plays a crucial role in reducing reliance on traditional fuels such as biomass and paraffin, which are commonly used for cooking, lighting, and heating in many developing countries. These fuels are often expensive, inefficient, and associated with health and environmental risks. Solar energy systems can provide clean and sustainable alternatives, reducing the dependence on these polluting fuels and improving the health and well-being of communities. Solar-powered lighting, for example, can replace hazardous kerosene lamps, reducing indoor air pollution and related health risks, particularly for women and children who are disproportionately affected by indoor air pollution.
In addition to providing reliable electricity and reducing reliance on traditional fuels, solar energy can also contribute to improving livelihoods in developing countries. Access to electricity can enable income-generating activities such as small businesses, agri-processing, and productive use of electricity in rural areas. Solar-powered irrigation systems can improve agricultural productivity and enhance food security, contributing to poverty reduction and economic development. Solar energy can also create employment opportunities in the solar industry, providing local job opportunities and promoting economic growth in developing countries.

Off-Grid Solar Systems:
Off-grid solar systems are gaining traction in developing countries as a means to provide electricity to remote and off-grid areas. Their benefits include providing reliable and sustainable electricity to underserved communities, enabling rural electrification, innovative business models, and technological advancements. Off-grid solar systems have the potential to contribute to poverty alleviation, promote economic development, and accelerate progress towards achieving universal energy access in developing countries.
Rural electrification is a crucial application of off-grid solar systems. In many developing countries, a significant portion of the population lives in rural areas where electricity access is limited or non-existent. Off-grid solar systems can provide electricity for lighting, powering appliances, and running productive activities such as small businesses and agri-processing. Access to electricity can improve education, healthcare, and economic opportunities in rural communities, contributing to poverty alleviation and sustainable development. Off-grid solar systems also have the potential to accelerate progress towards achieving the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 7 of ensuring access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all.
Innovative business models are driving the adoption of off-grid solar systems in developing countries. Pay-as-you-go (PAYG) and mobile money-based models have gained popularity, allowing customers to access solar energy on a pay-per-use basis, making it affordable and accessible to low-income households. These models have enabled increased affordability and flexibility in payment options, making solar energy systems more accessible to underserved communities. Furthermore, local entrepreneurs and micro-entrepreneurs are also leveraging off-grid solar systems to establish energy-based businesses, such as charging stations, solar-powered water pumping stations, and solar-powered cold storage facilities, creating local job opportunities and promoting economic development.
Technological advancements are also driving the growth of off-grid solar systems in developing countries. Improvements in solar panel efficiency, battery storage technologies, and power electronics have increased the reliability and performance of off-grid solar systems, making them more suitable for remote and off-grid environments. Internet of Things (IoT) technologies are being integrated into off-grid solar systems, allowing for remote monitoring, maintenance, and payment collection. These technological advancements are further enhancing the scalability and sustainability of off-grid solar systems, making them a viable solution for addressing electricity access challenges in developing countries.
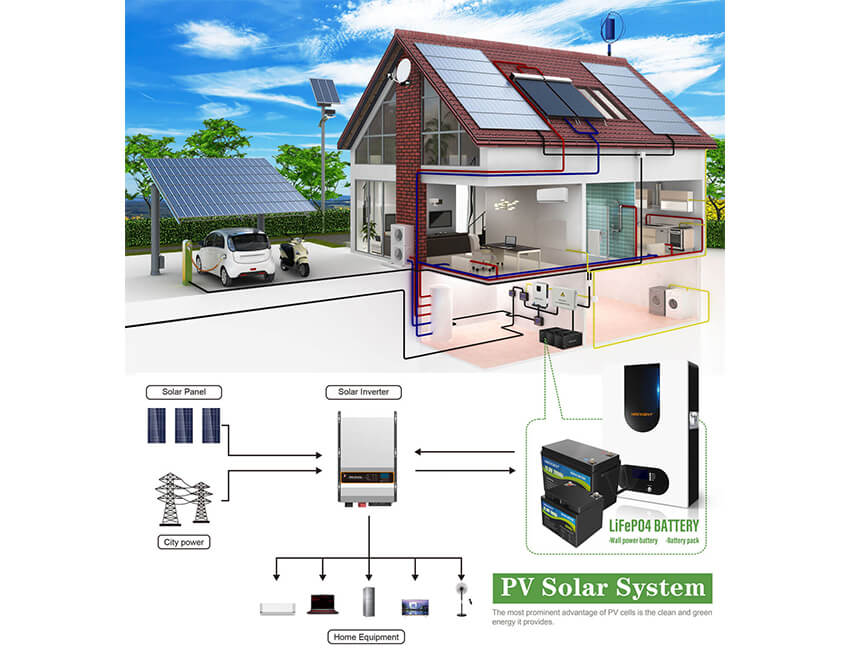
Community Solar Projects:
Community solar projects are gaining traction in developing countries as an innovative and sustainable way to harness solar energy. These projects involve multiple households or communities coming together to share the benefits of a solar energy system. The advantages of community solar projects are numerous and can range from increased access to renewable energy, community engagement, innovative financing models, and supportive policy frameworks.
One of the significant advantages of community solar projects is the increased access to renewable energy. In many developing countries, access to electricity is limited, and communities may rely heavily on fossil fuels or traditional biomass for their energy needs. Community solar projects provide an opportunity for communities to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. By pooling resources and sharing the costs of installing and maintaining solar panels, households or communities can generate their own electricity, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and contributing to a greener future. This increased access to renewable energy can improve the quality of life for community members, powering schools, health clinics, and other essential services, and spurring economic development.
Community engagement is another key aspect of community solar projects. These projects involve active participation and cooperation among community members, fostering a sense of ownership and pride in the solar energy system. Community members are involved in decision-making processes, such as selecting the location of solar panels and determining how the electricity generated will be used and shared among households or community facilities. This engagement can lead to increased awareness and education about renewable energy, promoting sustainable practices and behaviors within the community. Moreover, community solar projects can create social cohesion and strengthen community ties, as they require collaboration and mutual support among community members.
Financing models play a crucial role in the success of community solar projects. Many developing countries face financial constraints, and the high upfront costs of installing solar panels can be a significant barrier to adoption. However, community solar projects often utilize innovative financing models that make solar energy more affordable and accessible to communities. For example, crowdfunding, community-based loans, and cooperative models can be used to finance the installation and maintenance of solar panels. These financing models distribute the costs among community members, making it more affordable for individual households or communities to participate in the project. Additionally, community solar projects can generate income through the sale of excess electricity to the grid, which can help offset the costs of the project over time.
Supportive policy frameworks are also essential for the success of community solar projects. Governments and policymakers can play a crucial role in creating an enabling environment that promotes community solar initiatives. This can include providing incentives such as tax credits or subsidies for community solar projects, simplifying regulations and permitting processes, and establishing feed-in tariffs or net metering policies that allow communities to sell excess electricity back to the grid. These policy measures can reduce barriers and create favorable conditions for community solar projects to thrive, encouraging more communities to embrace renewable energy and contribute to sustainable development.








