Contents:
How Solar Panels Charge Batteries
Types of Batteries Suitable for Solar Charging
Factors Affecting the Efficiency of Charging
Benefits of Using Solar Panels to Charge Batteries
Challenges to Consider
Battery Types for Solar Charging
Additional Considerations for Solar Battery Charging Systems
FAQs
Solar energy is a clean, renewable source of energy that is becoming more popular for powering a variety of devices and systems. The most widely used application of solar energy is in battery charging, in which the energy is stored and can be used later. As such, solar panels are perfect for off-grid operations, EVs, and even portable applications. This article will look at how solar panels charge batteries, the battery chemistry types that are most compatible with solar charging, and what effects charging efficiency.
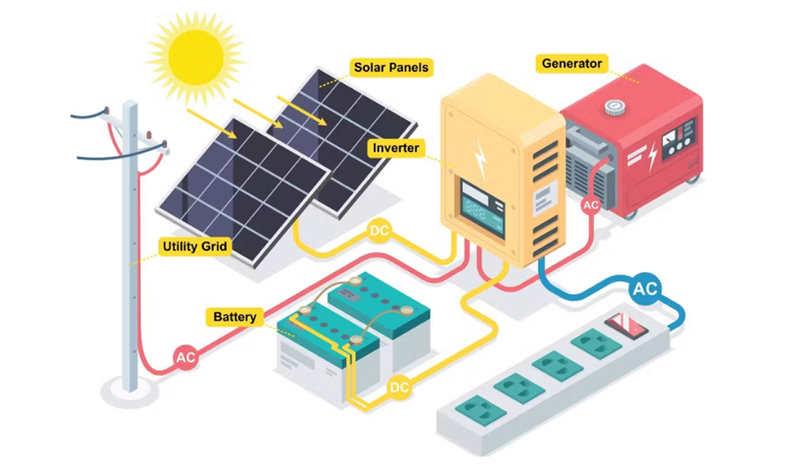
How Solar Panels Charge Batteries
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells. When sunlight hits the PV cells, electrons are excited, generating an electric current. That current is then used to recharge batteries. There are some key aspects involved in the process:
-
Solar panels: These capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
-
Charge Controller: A charge controller regulates the flow of electricity from the solar panel to the battery, ensuring that the battery is not overcharged or damaged.
-
Battery: A battery stores the electricity produced by the solar panels for use later when the sun is not shining.
-
Inverter (if necessary): If you have AC-powered devices, you need an inverter to convert the battery's DC electricity into alternating current (AC).
Types of Batteries Suitable for Solar Charging
Some batteries are not meant for solar charging. There are many types, but here are the types most commonly used:
-
Lead-Acid Batteries: They are economical and common for most of the off-grid solar systems but have lesser lifespan and efficiency in comparison to newer battery types.
-
Lithium-ion Battery: More efficient, longer-lasting, and higher-performing but most costly. Their use in solar energy storage is on the rise.
-
Lithium Iron Phosphate in short LiFePO4: These are a class of lithium-ion batteries that provide high safety, long cycle life and durability, meaning these batteries are suitable for solar applications.
-
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries: While not as common because of their environmental impact and cost, NiCd batteries remain in some solar-powered applications.
Factors Affecting the Efficiency of Charging
Several factors can influence how well solar panels charge batteries:
-
Solar Panel Efficiency: The more efficient the solar panel, the faster it can convert sunlight into electricity to charge the battery.
-
Battery Capacity: Larger batteries (measured in ampere-hours, Ah) take longer to charge but can store more energy.
-
Sunlight Availability: The amount of sunlight available directly affects how quickly a battery can be charged. Regions with more sunlight will see faster charging.
-
Charge Controller: A high-quality charge controller optimizes the charging rate and prevents overcharging, which could damage the battery.
-
Temperature: Extreme temperatures can negatively impact both the performance of solar panels and the efficiency of batteries. Solar panels generally perform better in cooler temperatures, while extreme heat or cold can reduce battery efficiency.
Benefits of Using Solar Panels to Charge Batteries
-
Renewable Energy: Solar energy is sustainable and eco-friendly, providing a clean alternative to fossil fuels.
-
Cost Savings: Solar panels, after initial installation, provide substantially decreased costs for electricity.
-
Grid Independence: In remote or outlying locations, where access to grid power is limited, they can also reduce reliance on grid power.
-
Environmentally Friendly: Using solar energy reduces carbon footprints and helps fight climate change.
Challenges to Consider
-
Initial Investment: The cost of installing solar panels, batteries, and other components can be high.
-
Space Requirements: Solar panels require a substantial amount of space, especially for larger systems that store more energy.
-
Weather Dependency: Solar energy generation depends on sunlight, so cloudy or rainy weather can reduce charging efficiency.
-
Battery Lifespan: While newer batteries last longer than traditional lead-acid ones, they still have a limited lifespan and will eventually need to be replaced.
Battery Types for Solar Charging
|
Battery Type
|
Pros
|
Cons
|
Ideal For
|
|
Lead-Acid Batteries
|
Low cost, widely available
|
Shorter lifespan, lower efficiency
|
Budget-conscious off-grid systems
|
|
Lithium-Ion Batteries
|
Longer lifespan, high efficiency, lightweight
|
Higher initial cost
|
Residential and commercial solar systems
|
|
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate)
|
Long lifespan, stable, safe
|
Expensive compared to lead-acid
|
High-efficiency solar storage systems
|
|
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries
|
Durable, performs well in extreme conditions
|
High cost, environmental impact
|
Specialized applications, less common
|
Additional Considerations for Solar Battery Charging Systems
While solar energy offers numerous benefits for charging batteries, there are still some technical and practical considerations that users should be aware of when setting up their solar charging systems.
Sizing and designing the solar panel battery charger system is one of the most vital aspects. This involves choosing the appropriate number of solar panels, batteries, and charge controllers, given the energy needs.
-
Size of Solar Panels: The powering of solar panels is dependent on its size and efficiency. Higher power panels will generate more electricity, but will take up more space.
-
Battery Size: The battery should deliver the energy requirements of the system. A battery that is too small will not store enough energy, while one that is too large may cause undercharging, which will reduce its life.
-
Ownership of the system: Consider if you want to own the system, so that you could provide the electricity to others, for example if they do not have a convection oven or something similar. Controllers that are undersized or oversized can damage the system, so getting one with correct specifications is critical.
Although solar battery systems are relatively low maintenance, they do require some attention to ensure a long lifespan and together peak performance. Solar panels and batteries need to be kept in good condition to function properly and require regular maintenance.
-
Solar Panels: Dust, debris, and other environmental factors can affect solar panel efficiency, and keeping them clean can make a positive electronic difference. It is also advised to periodically check the panels to see if they are damaged, scratched, or worn.
-
Batteries: Batteries, especially lead-acid and lithium-ion types, need to be checked for proper charge levels and health. If the batteries are overcharged or deep discharged, it will spoil the battery and reduce cycle life. Keep battery terminals clean and free of corrosion.
The temperature is one of the important parameters influencing the operational performance and service life of batteries. Both extreme hot and extreme cold can make batteries run poorly or not last as long.
-
Hot Climatic Zones: Install the batteries in a shaded or temperature-controlled environment in hot climatic zones. At high temperatures, batteries may overheat, limiting capability and performance.
-
Cold Climates: In cold environments, batteries can become less efficient and may need a heating solution to maintain proper function. Some advanced systems include battery heaters or insulation to protect batteries from freezing temperatures.
In many off-grid scenarios, solar panels are only part of a larger energy generation system. They can be powered by a mixture of solar power and renewable energy sources (wind or hydroelectric) to top-up batteries.
-
Hybrid systems: Hybrid systems consists of a type of renewable energy such as solar panels combined with wind turbines or some other renewable sources to always have energy even though sunlight is not available. For example, a battery bank is able to store excess energy generated at peak conditions for use at times when power usage is at a minimum.
-
A grid tied system: The balance between pure solar power and grid power, a grid tied system allows you to charge batteries using grid electricity if there is insufficient solar power. It could ensure that the battery never runs out even on a cloudy or rainy day.
Chargers that can quick charge batteries using solar panels are a sustainable and efficient solution for a variety of applications, from off-grid living to electric vehicles and portable devices. The right components, care and knowledge of charging efficiency factors will help users improve their solar powered battery systems for long-lasting peak performance. With continual advancements in technology, solar energy batteries will simply become more efficient, offering increased energy independence and a greener tomorrow.
FAQs






