In today's modern world, lithium-ion batteries power everything from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and even airplanes. Their energy density, long life, and efficiency make them the go-to power source for portable electronics and green technology. But every so often, headlines emerge about a phone catching fire, a hoverboard exploding, or an electric vehicle engulfed in flames. These events often raise alarm bells with a single question: Do lithium batteries explode?
The short answer is yes, under certain conditions, lithium batteries can explode or catch fire. However, it’s important to put this in context. Explosions or fires involving lithium batteries are rare and usually the result of manufacturing defects, misuse, or extreme conditions. This article explores why lithium batteries can explode, what causes these incidents, how often they actually happen, and what manufacturers and users can do to minimize the risks.
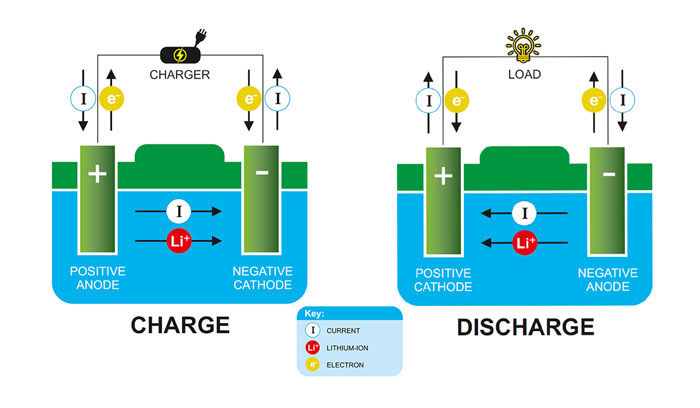
1. How Do Lithium Batteries Work?
To understand why they might explode, it's helpful to first understand how lithium-ion batteries function.
A lithium-ion battery typically consists of the following components:
-
Anode (negative electrode) – usually made of graphite.
-
Cathode (positive electrode) – made of a lithium metal oxide.
-
Electrolyte – a liquid or gel that enables ions to flow between the anode and cathode.
-
Separator – a barrier that keeps the anode and cathode from touching, which would cause a short circuit.
When a device is in use, lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte, releasing energy. When charging, the ions move in the opposite direction.
While efficient, this design is not without risk. If the internal structure is damaged or compromised, or if the battery is overcharged or overheated, a thermal runaway event can occur, leading to fire or explosion.

2. What Is Thermal Runaway?
Thermal runaway is the key mechanism behind most lithium battery explosions.
It occurs when the battery's internal temperature increases rapidly due to a fault (like internal short-circuiting), causing a chain reaction:
-
The heat causes the electrolyte to decompose, releasing flammable gases.
-
The temperature rise accelerates chemical reactions within the cell.
-
Eventually, the pressure from the gas buildup can cause the battery to vent, rupture, or explode.
This process can be triggered by several factors, including:
-
Physical damage (e.g., dropping the device).
-
Overcharging the battery.
-
Using non-approved chargers.
-
Exposure to high temperatures (e.g., leaving a phone in a hot car).
-
Manufacturing defects.
3. Real-World Incidents and Statistics
Despite the headlines, lithium battery explosions are quite rare relative to the number of batteries in use.
For example, according to a report from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), between 2006 and 2023, there were about 400 confirmed battery fire incidents on aircraft in the U.S. That number sounds high until you consider that over 3 billion lithium-ion batteries are shipped each year worldwide.
Some high-profile incidents include:
-
Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Recall (2016): One of the most famous examples, where a design flaw caused internal short circuits, leading to dozens of fires and a global recall.
-
Tesla Car Fires: A few cases of Teslas catching fire after crashes or battery damage have made headlines, though these events remain rare relative to the number of vehicles sold.
-
Hoverboard Fires (2015–2016): Inexpensive and poorly manufactured hoverboards were linked to hundreds of fire reports, leading to recalls and regulatory action.
These incidents highlight that while the risk exists, it is often linked to design flaws, quality control issues, or misuse, rather than an inherent instability of lithium batteries themselves.
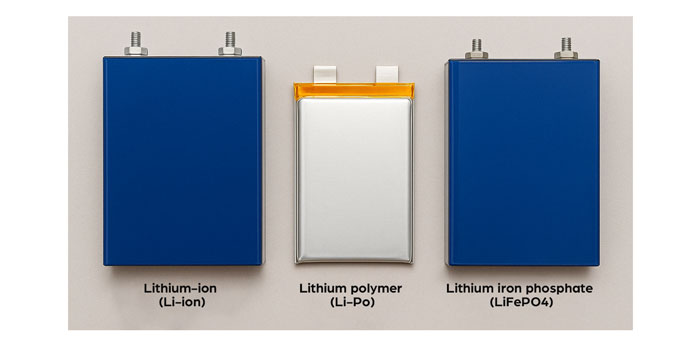
4. Types of Lithium Batteries and Safety
It’s worth noting that not all lithium batteries are created equal. There are several types, including:
-
Lithium-ion (Li-ion): Most common in consumer electronics.
-
Lithium polymer (Li-Po): Used in drones, smartphones, and RC vehicles; more flexible in shape but slightly more sensitive to punctures.
-
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4): More stable, used in electric vehicles and solar storage systems.
LiFePO4 batteries, for example, are known for their thermal stability and are much less prone to fire than other lithium chemistries.
Manufacturers now build multiple safety features into lithium battery packs, including:
-
Battery Management Systems (BMS): Prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and overheating.
-
Thermal fuses and separators: Shut down the battery when temperatures rise too high.
-
Fire-resistant casings: Delay the spread of fire in the event of failure.
5. How to Prevent Lithium Battery Explosions
Although you can't eliminate the risk completely, there are practical steps consumers can take to minimize the chances of a battery fire or explosion:
Use Approved Chargers:
Always use the charger provided by the manufacturer or one that’s certified for your device. Cheap third-party chargers can deliver the wrong voltage or current.
Avoid Overcharging:
Most modern devices stop charging automatically, but it’s still good practice not to leave devices plugged in overnight regularly.
Don't Expose to Heat:
Avoid leaving electronics in hot cars or under direct sunlight for extended periods.
Inspect Batteries:
If a battery appears swollen, leaking, or discolored, stop using it immediately and dispose of it properly.
Avoid Physical Damage:
Don’t puncture or crush devices. If you drop your phone or laptop and it starts to overheat or swell, it could be a sign of internal damage.
Proper Storage and Disposal:
Store batteries in a cool, dry place. When disposing of them, follow local guidelines—never throw lithium batteries in the trash.
Conclusion
So, do lithium batteries explode? Yes—but rarely, and usually under preventable circumstances. The overwhelming majority of lithium batteries operate safely throughout their lifespan, powering the devices we depend on every day.
Understanding how they work, how they can fail, and how to handle them safely can significantly reduce your risk. Manufacturers, regulators, and consumers all play a role in making battery-powered technology both powerful and safe.








