Contents:
Ionic lithium batteries have revolutionized energy storage, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles (EVs). Their high energy density, long lifespan, and lightweight design make them a cornerstone of modern technology. This article provides an in-depth look at these batteries, exploring their structure, benefits, applications, and future prospects.
What Are Ionic Lithium Batteries?
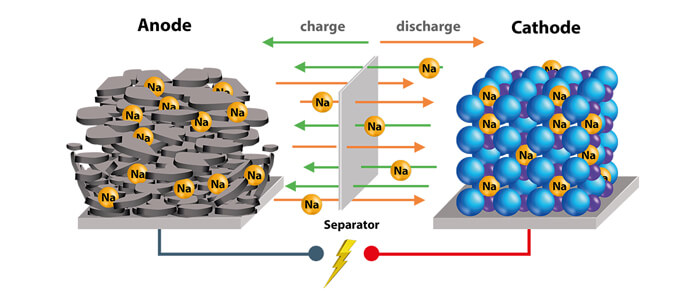
Ionic lithium batteries, commonly referred to as lithium-ion batteries, are rechargeable power storage devices. They rely on lithium ions moving between the anode (typically made of graphite) and cathode (often composed of lithium metal oxides) to store and discharge energy.
Key Components:
-
Anode: Stores lithium ions during discharge.
-
Cathode: Releases lithium ions during discharge.
-
Electrolyte: Facilitates ion movement between electrodes.
-
Separator: Prevents direct contact between anode and cathode while allowing ion flow.
How Do They Work?
Ionic lithium batteries operate on the principle of ion exchange:
-
Charging: Lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode, storing energy.
-
Discharging: Lithium ions flow back to the cathode, releasing energy.
The reversible nature of this process ensures multiple charge-discharge cycles, contributing to their popularity.
Advantages of Ionic Lithium Batteries
-
High Energy Density: They store more energy per unit weight than other battery types.
-
Long Cycle Life: Supports hundreds to thousands of charge cycles.
-
Low Self-Discharge: Retains charge for extended periods when not in use.
-
Lightweight: Ideal for portable and electric vehicle applications.
-
Eco-Friendly: Recyclable components reduce environmental impact.
Applications of Ionic Lithium Batteries
Ionic lithium batteries are versatile, powering various sectors:
-
Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, and cameras.
-
Electric Vehicles (EVs): Cars, bikes, and scooters.
-
Renewable Energy Storage: Solar and wind energy systems.
-
Medical Devices: Portable diagnostic tools and implants.
-
Industrial Equipment: Forklifts, drones, and robotic machinery.
Performance Trends and Capacity
Challenges and Safety Concerns
Despite their advantages, ionic lithium batteries face some challenges:
-
Thermal Runaway: Overcharging or puncturing can lead to overheating and fires.
-
Raw Material Supply: Dependence on lithium mining raises ethical and environmental concerns.
-
Recycling: Although possible, the recycling process is costly and energy-intensive.
Comparison of Ionic Lithium Batteries with Other Battery Types
To understand the advantages of ionic lithium batteries, comparing them with other common battery technologies can provide valuable insights. Below is a table highlighting key differences:
| Feature |
Lithium-Ion |
Lead-Acid |
Nickel-Cadmium |
| Energy Density (Wh/kg) |
150–280 |
30–50 |
40–60 |
| Cycle Life |
500–3,000 |
200–500 |
1,000+ |
| Weight |
Light |
Heavy |
Moderate |
| Self-Discharge Rate (%/month) |
2–5% |
5–10% |
10–20% |
| Environmental Impact |
Moderate |
High |
High |
Global Market Overview of Ionic Lithium Batteries
The demand for ionic lithium batteries has grown exponentially due to the rise of electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and portable electronics. Below is a table summarizing the key market statistics for 2024:
| Region |
Market Share (%) |
Key Application |
Growth Rate (CAGR) |
| Asia-Pacific |
45% |
Electric Vehicles |
12.5% |
| North America |
25% |
Renewable Energy Storage |
9.8% |
| Europe |
20% |
Consumer Electronics |
8.2% |
| Rest of the World |
10% |
Industrial Applications |
6.7% |
Sustainability and Recycling Initiatives
As ionic lithium batteries become a central component of modern energy systems, sustainable practices are increasingly critical. Current efforts include:
-
Enhanced Recycling Technologies: Efficiently recovering valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
-
Battery Second-Life Applications: Repurposing used EV batteries for energy storage in homes and businesses.
-
Eco-Friendly Manufacturing: Reducing reliance on harmful chemicals and energy-intensive processes.
These initiatives not only mitigate environmental impacts but also help secure a stable supply of raw materials for future production.
Potential Disruptions in the Market
Several factors could influence the trajectory of ionic lithium battery development:
-
Advances in Competing Technologies: Innovations in hydrogen fuel cells or alternative energy storage systems could pose challenges.
-
Supply Chain Constraints: Geopolitical factors and mining restrictions may disrupt material availability.
-
Regulatory Changes: Stricter environmental regulations could affect production processes and market dynamics.
Adapting to these challenges will be essential for maintaining the dominance of ionic lithium batteries in the global energy landscape.
FAQs About Ionic Lithium Batteries
What makes ionic lithium batteries better than other battery types?
Ionic lithium batteries excel in energy density, lifespan, and weight, making them ideal for modern applications like EVs and portable electronics.
Are ionic lithium batteries safe to use?
Yes, they are safe when used properly, but mishandling, overcharging, or physical damage can lead to overheating or fires.
How long do ionic lithium batteries last?
They typically last 500–3,000 charge cycles, depending on usage and care.
Can ionic lithium batteries be recycled?
Yes, most components, including lithium, cobalt, and nickel, can be recycled to reduce environmental impact.
What are the primary applications of ionic lithium batteries?
They power devices like smartphones, laptops, EVs, renewable energy systems, and medical equipment.






