Contents:
Solar energy is gaining traction in Zambia as a sustainable solution for energy needs. Whether for residential or commercial use, proper connection of solar panels ensures maximum efficiency and performance. This guide provides a clear explanation and a color-coded table to aid in understanding solar panel connections.
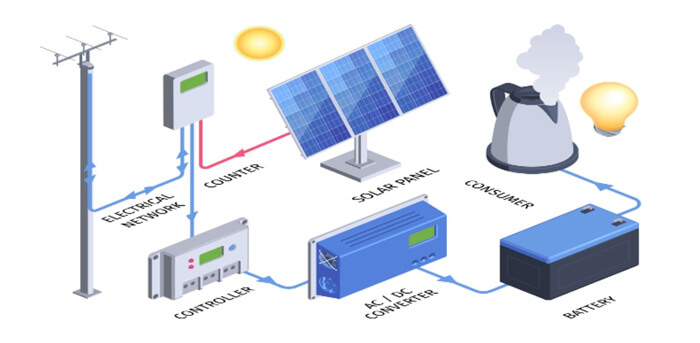
Key Elements of a Solar Panel Connection Diagram
-
Solar Panels: These collect sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
-
Charge Controller: Protects batteries from overcharging and manages power input.
-
Battery Bank: Stores electricity for use when sunlight is unavailable.
-
Inverter: Converts DC electricity into alternating current (AC) for appliances.
-
Load: The appliances and devices that consume the electricity.
Types of Solar Panel Connections
-
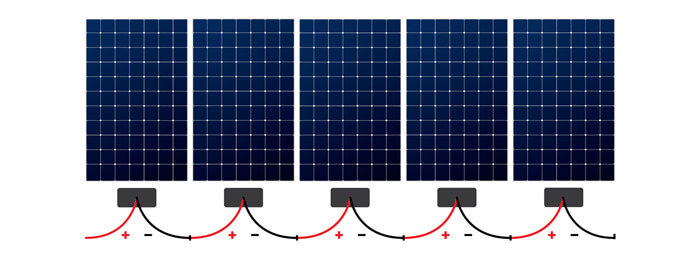
Series Connection: Increases voltage while keeping current constant. Suitable for high-voltage systems.
-
Parallel Connection: Increases current while keeping voltage constant. Ideal for systems requiring more power at a stable voltage.
-
Hybrid Connection: Combines series and parallel configurations to balance voltage and current.
Table: Solar Panel Connection Components
| Component |
Purpose |
Description |
| Solar Panels |
Captures solar energy |
Mono/polycrystalline panels of 12V or 24V |
| Charge Controller |
Regulates voltage/current |
PWM or MPPT controllers for efficiency |
| Battery Bank |
Stores electricity |
Lithium-ion or lead-acid batteries |
| Inverter |
Converts DC to AC |
Pure sine wave inverters recommended |
| Load |
Consumes electricity |
Lights, fans, refrigerators, and pumps |
Steps to Connect Solar Panels
-
Design the System: Determine power requirements and the number of solar panels needed.
-
Mount the Panels: Place them at an optimal angle for maximum sunlight exposure.
-
Connect the Panels: Use either series or parallel connections as per system design.
-
Install the Charge Controller: Link it between the panels and battery bank to regulate power.
-
Set Up the Battery Bank: Connect batteries to store energy effectively.
-
Integrate the Inverter: Connect it to the battery bank and the load for AC power supply.
By following these guidelines, Zambian users can ensure a seamless solar installation process, optimized for local conditions. The table highlights essential components and their roles, simplifying system setup for beginners and professionals alike.
Wiring Techniques for Solar Panel Systems
1. Selecting the Correct Wires
-
Use wires rated for outdoor use, resistant to UV rays and moisture.
-
Ensure the wire gauge matches the system's current capacity to prevent overheating.
2. Connecting Solar Panels in Series
3. Connecting Solar Panels in Parallel
Safety Tips During Installation
-
Turn Off Equipment: Disconnect all power sources before wiring.
-
Use Proper Tools: Ensure you have crimping tools, insulated screwdrivers, and multimeters.
-
Ground the System: Install an earthing rod to prevent electric shocks and protect from lightning.
-
Inspect Connections: Double-check all connections to avoid short circuits or loose wires.
Solar Panel Setup Considerations in Zambia
-
Geographical Orientation: Align panels to face north for optimal sunlight exposure in the Southern Hemisphere.
-
Tilt Angle: Adjust the tilt to match Zambia’s latitude (approximately 15°) for maximum efficiency.
-
Seasonal Adjustments: Reposition panels slightly during rainy seasons to improve performance.
-
Dust and Maintenance: Clean panels regularly to remove dust and debris that reduce output.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
|
Issue
|
Cause
|
Solution
|
|
Low Energy Output
|
Shading, dirt on panels
|
Remove obstructions, clean panels
|
|
Battery Not Charging
|
Faulty controller or wiring issue
|
Inspect controller, check connections
|
|
Inverter Malfunction
|
Overload or incorrect wiring
|
Reduce load, verify wiring configuration
|
|
Overheating Wires
|
Undersized wires
|
Replace with thicker wires
|
Solar installations tailored to Zambia’s climatic and energy needs can greatly enhance energy independence. Following proper wiring techniques and installation practices ensures long-lasting and reliable systems.
Maintenance Practices for Solar Panel Systems
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of solar panel systems, regular maintenance is essential.
1. Cleaning Solar Panels
-
Frequency: Clean panels every 2-4 weeks, depending on dust levels.
-
Method: Use soft brushes or cloths with water to avoid scratching. Avoid abrasive materials.
2. Inspecting Electrical Components
3. Monitoring System Performance
4. Protecting Batteries
-
Keep batteries in a cool, ventilated space.
-
Avoid deep discharges by using a charge controller with proper cutoff settings.
Regulatory and Incentive Landscape in Zambia
Zambia offers several incentives to promote the adoption of solar energy:
-
Net Metering: Allows users to sell excess electricity back to the grid.
-
Tax Exemptions: Reduced or no import duty on solar equipment and components.
-
Subsidy Programs: Government or NGO-led programs providing affordable solar solutions for rural areas.
Compliance with Zambia Bureau of Standards (ZABS) regulations is crucial for imported and locally assembled solar products.
Designing for Scalability
When installing a solar system, consider future scalability to accommodate increased energy demands.
1. Modular Panel Arrays
2. Battery Bank Expansion
3. Upgradable Inverter Capacity
Solar panel systems in Zambia have the potential to transform energy accessibility across urban and rural regions. By integrating efficient wiring, regular maintenance, and scalable designs, these systems can deliver reliable and sustainable energy solutions for decades.
FAQs About Solar Panel Connection in Zambia







