1. Strategies for Effective Implementation of Solar Systems in South Africa
Solar energy has emerged as a promising renewable energy source with the potential to address South Africa's energy challenges, including increasing electricity demand, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and improving energy access in rural communities. However, the successful implementation of solar systems in South Africa requires effective policies that promote their adoption and address potential barriers. This paper critically analyzes the existing implementation policies for solar systems in South Africa, evaluates their effectiveness, and proposes recommendations for improvement.
The paper begins with an overview of the current energy landscape in South Africa, highlighting the need for renewable energy solutions to meet the country's growing energy demands while reducing its reliance on fossil fuels. It then reviews the existing policies and regulations related to solar systems, including the Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Program (REIPPPP) and the Integrated Resource Plan (IRP), which provide a framework for renewable energy development in the country. The paper assesses the strengths and weaknesses of these policies, including issues related to policy stability, grid integration, financing, and community participation.
Drawing on international best practices and lessons learned from other countries' experiences, the paper proposes recommendations to enhance the effectiveness of implementation policies for solar systems in South Africa.
- Policy stability and long-term planning: Providing a stable and predictable policy environment is critical to attract investment in solar systems. The paper recommends establishing a long-term plan for renewable energy development, with clear targets and timelines, and avoiding abrupt policy changes that can create uncertainty for investors.
- Grid integration and infrastructure development: Grid integration is a crucial aspect of solar system implementation. The paper suggests investing in grid infrastructure, including upgrading transmission and distribution networks, to accommodate increasing solar energy capacity. It also emphasizes the importance of developing energy storage solutions to address intermittency challenges.
- Financing mechanisms and incentives: Access to affordable financing is a key factor in promoting the adoption of solar systems. The paper recommends exploring innovative financing mechanisms, such as green bonds, tax incentives, and concessional loans, to facilitate investment in solar projects. It also highlights the need to prioritize financing options for underserved communities to ensure equitable access to solar energy benefits.
- Community participation and empowerment: Engaging local communities in the planning, development, and operation of solar projects can foster social acceptance and maximize local benefits. The paper suggests incorporating community participation mechanisms, such as community ownership models, job creation programs, and skills development initiatives, in solar system implementation policies.
- Capacity building and knowledge sharing: Building local capacity and expertise in solar energy technologies and project development is crucial for the sustainable growth of the sector. The paper recommends investing in education, training, and research to develop a skilled workforce and promote knowledge sharing among stakeholders.

Solar Systems in South Africa
2. Policy Frameworks for Solar System Implementation in South Africa
As South Africa strives to meet its increasing energy demands while mitigating climate change impacts, solar energy has emerged as a promising renewable energy source. The successful implementation of solar systems in the country requires robust policy frameworks that provide a supportive environment for solar energy development. This paper critically examines the existing policy frameworks for solar system implementation in South Africa, evaluates their effectiveness, and proposes recommendations for enhancing their impact.
The paper begins with an overview of the energy landscape in South Africa, highlighting the need for renewable energy solutions to diversify the energy mix, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and improve energy access. It then reviews the current policy frameworks, including the Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Program (REIPPPP), the Integrated Resource Plan (IRP), and other relevant policies and regulations. The paper evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of these policies, including their impact on solar energy deployment, investment attractiveness, and socio-economic benefits.
Drawing on international best practices and lessons learned from other countries' experiences, the paper proposes recommendations to enhance the effectiveness of policy frameworks for solar system implementation in South Africa.
- Policy stability and clarity: Providing a stable and transparent policy environment is crucial to attract investment in solar energy. The paper recommends ensuring policy stability and clarity, with clear targets, timelines, and incentives for solar energy development. Avoiding abrupt policy changes and addressing regulatory uncertainties can provide greater investor confidence and facilitate solar system implementation.
- Grid integration and infrastructure development: Grid integration is a critical aspect of solar system implementation. The paper suggests investing in grid infrastructure, including transmission and distribution networks, to accommodate increasing solar energy capacity. It emphasizes the need for adequate planning and coordination among relevant stakeholders to ensure smooth integration of solar energy into the grid.
- Financing mechanisms and incentives: Access to affordable financing is a key factor in promoting solar energy adoption. The paper recommends exploring innovative financing mechanisms, such as feed-in tariffs, tax incentives, and green bonds, to attract private sector investment in solar projects. It also emphasizes the importance of providing financing options for underserved communities and small-scale solar projects to promote inclusivity and equitable access to solar energy benefits.
- Local content and job creation: Maximizing local content and job creation can foster socio-economic development and support local industries. The paper suggests incorporating local content requirements in solar system implementation policies, including local procurement, manufacturing, and job creation targets. It also highlights the need for skills development programs and workforce training to support the growth of a skilled solar energy workforce in South Africa.
- Stakeholder engagement and community participation: Engaging relevant stakeholders and local communities is critical for the successful implementation of solar systems. The paper recommends incorporating stakeholder engagement and community participation mechanisms, such as public consultations, social impact assessments, and community ownership models, in solar system implementation policies. Ensuring meaningful participation of local communities can promote social acceptance and ownership of solar projects.
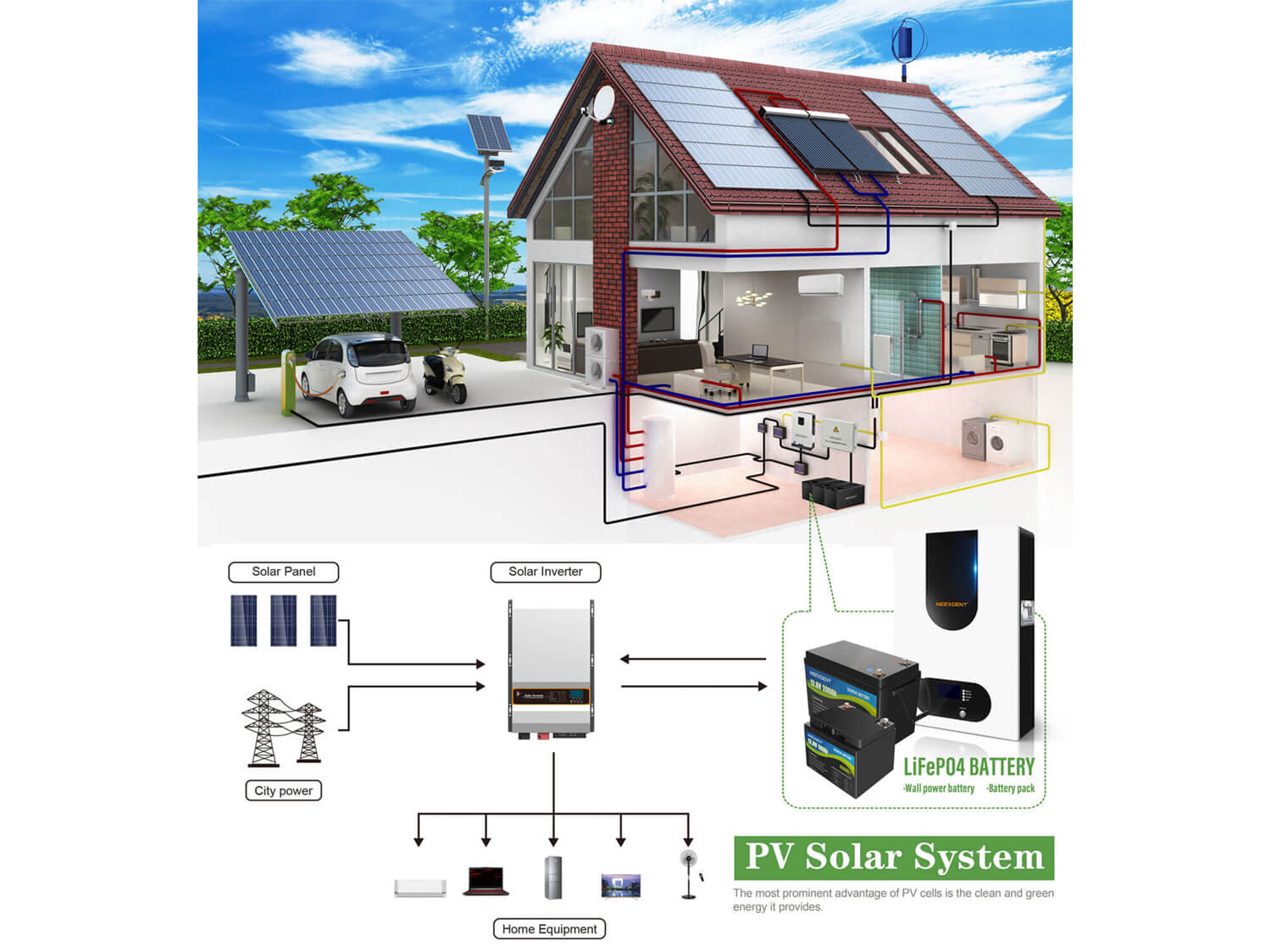
3. Enabling Solar Energy Adoption through Effective Implementation Policies in South Africa
Solar energy has gained significant attention as a promising renewable energy source to meet the increasing energy demands in South Africa while mitigating climate change impacts. The successful adoption of solar energy requires effective implementation policies that provide a conducive environment for solar energy development. This paper critically examines the existing implementation policies for solar energy in South Africa, evaluates their effectiveness, and proposes recommendations for enhancing their impact.
The paper begins with an overview of the energy landscape in South Africa, highlighting the potential of solar energy to diversify the energy mix, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and improve energy access. It then reviews the current implementation policies, including the Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Program (REIPPPP), the Integrated Resource Plan (IRP), and other relevant policies and regulations. The paper evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of these policies, including their impact on solar energy adoption, investment attractiveness, and socio-economic benefits.
Drawing on international best practices and lessons learned from other countries' experiences, the paper proposes recommendations to enhance the effectiveness of implementation policies for solar energy adoption in South Africa.
- Streamlining regulatory processes: Simplifying and streamlining regulatory processes can expedite solar energy project approvals and reduce administrative burdens. The paper recommends establishing a clear and efficient regulatory framework for solar energy projects, including streamlined permitting and licensing procedures, and reducing bureaucratic hurdles that may hinder solar energy development.
- Incentivizing solar energy investment: Providing incentives and financial mechanisms can attract private sector investment in solar projects. The paper suggests exploring options such as feed-in tariffs, tax incentives, and grants to promote solar energy adoption. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for innovative financing mechanisms, including green bonds and blended finance, to mobilize private capital for solar energy projects.
- Promoting local content and job creation: Maximizing local content and job creation can support economic development and promote social acceptance of solar energy projects. The paper recommends incorporating local content requirements in implementation policies, including local procurement, manufacturing, and job creation targets. It also highlights the importance of skills development programs and workforce training to support the growth of a skilled solar energy workforce in South Africa.
- Enhancing grid integration and infrastructure development: Grid integration is a critical aspect of solar energy adoption. The paper suggests investing in grid infrastructure, including transmission and distribution networks, to accommodate increasing solar energy capacity. It emphasizes the need for coordinated planning and development of grid infrastructure to ensure smooth integration of solar energy into the existing grid.
- Encouraging community participation and stakeholder engagement: Engaging local communities and relevant stakeholders is crucial for the successful adoption of solar energy. The paper recommends incorporating community participation and stakeholder engagement mechanisms, such as public consultations, social impact assessments, and community ownership models, in implementation policies. It highlights the need for meaningful engagement of local communities to ensure their participation and ownership of solar energy projects.







